This is an old revision of the document!
Cellular Potts models
Stem cells in the intestinal crypt
Introduction
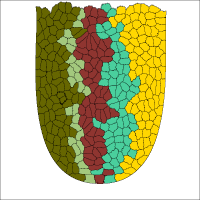
This illustrative example shows the emergence of clonal populations from stem cells in an intestinal crypt. Stem cells in the bottom of the crypt divide asymmetrically and produce a population of transit amplifying (TA) cells. For each of the TA cells, the color indicates the stem cell is it derived from.
Model description
This model shows several new modeling features, available as of Morpheus 1.2.
Loading domain from image
The crypt-like domain is specified by loading an external 8-bit TIFF image file using Lattice/Domain/Image.
Asymmetric cell division
Stem cells divide asymmetrically using the new ChildID handles in the Proliferation plugin. This sets a user-defined symbol (here called daughter) to either 1 or 2. This symbol can then be used to distinguish both daughter cells and treat them differently. In this example, it used to set the stemness (s) of one daughter to 1 and the stemness of the other daughter cell to 0.
Conditionally changing cell types
When a cell looses its stemness s, it is moved to the TA cell type. This is done using the new ChangeCellType plugin.
Upon satisfyiug its Condition, ChangeCellType moves the cell to the specified new cell type. By default, all the properties of a cell that exist in both cell type context are maintained and unspecified ones are set to their default values. This default behavior can be overridden using Triggers that specify Rules stating how to deal with specific properties.
PopulationReporter
The new PopulationReporter allows the collection of statistical data about the cell population. Here, it is used to count the sizes of the various clonal populations. This number of reported into a Global and subsequently written to file and plotted using a Logger.
Model
h Crypt.xml |h
extern>http://imc.zih.tu-dresden.de/morpheus/examples/CPM/Crypt.xml
In Morpheus GUI: Examples → CPM → Crypt.xml